Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models (DDPM) have been used extensively with great success in the vision field, with many models showing particularly high-quality results in image inpainting. We propose applying similar diffusion methods to the speech domain, with the goal of performing super-resolution on speech samples. We believe that an analogous method to image inpainting can be performed on low resolution speech samples to retrieve a target high-resolution sample. Throughout this study, we compare super-resolution results from multiple baseline models with an unconditional diffusion-based approach.
Listening samples for evaluation
We recommend using headphones for this section.
| 196-122150-0000 | 196-122150-0001 | |
|---|---|---|
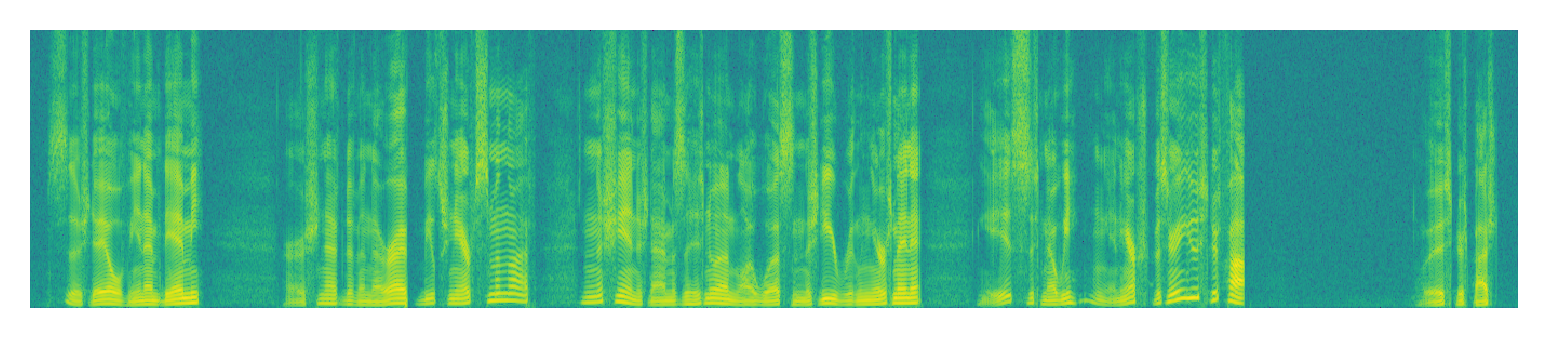 |
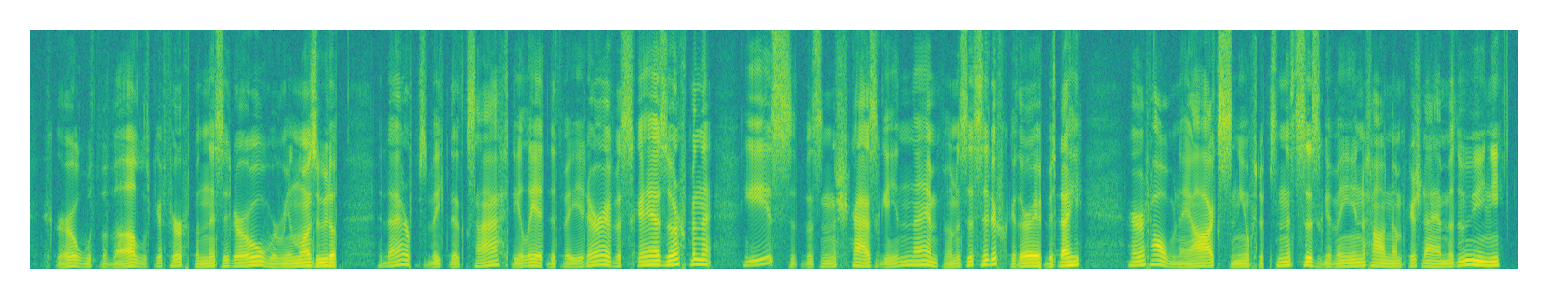 |
|
| Input | ||
 |
 |
|
| Target | ||
 |
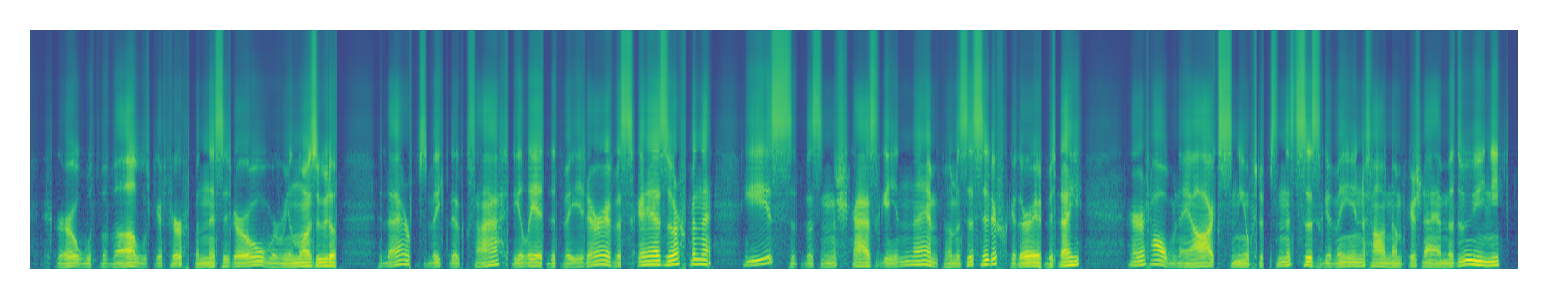 |
|
| LSTM | ||
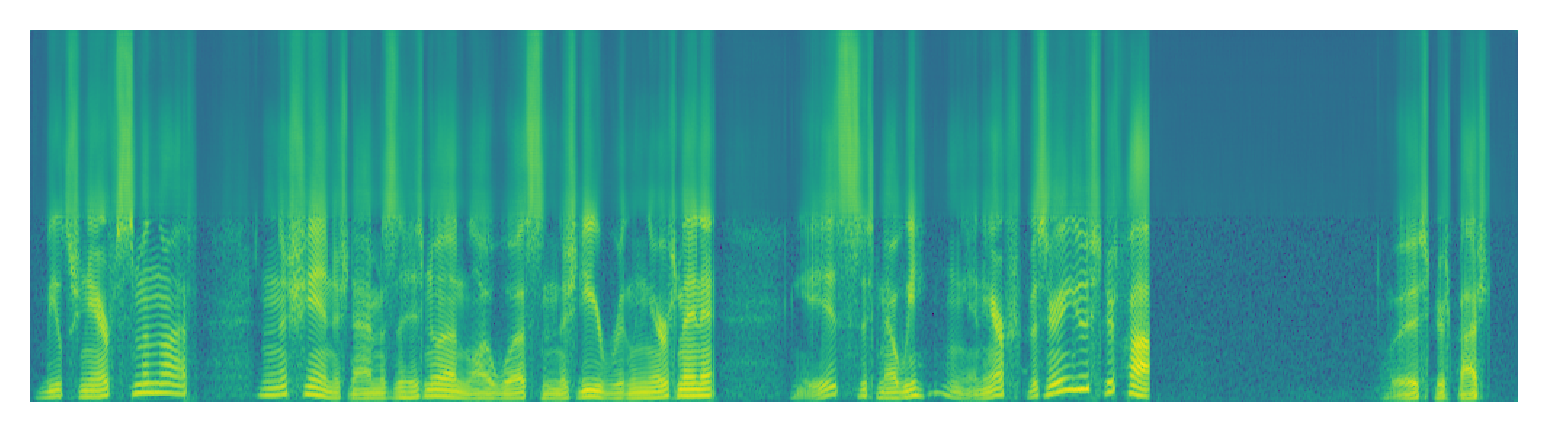 |
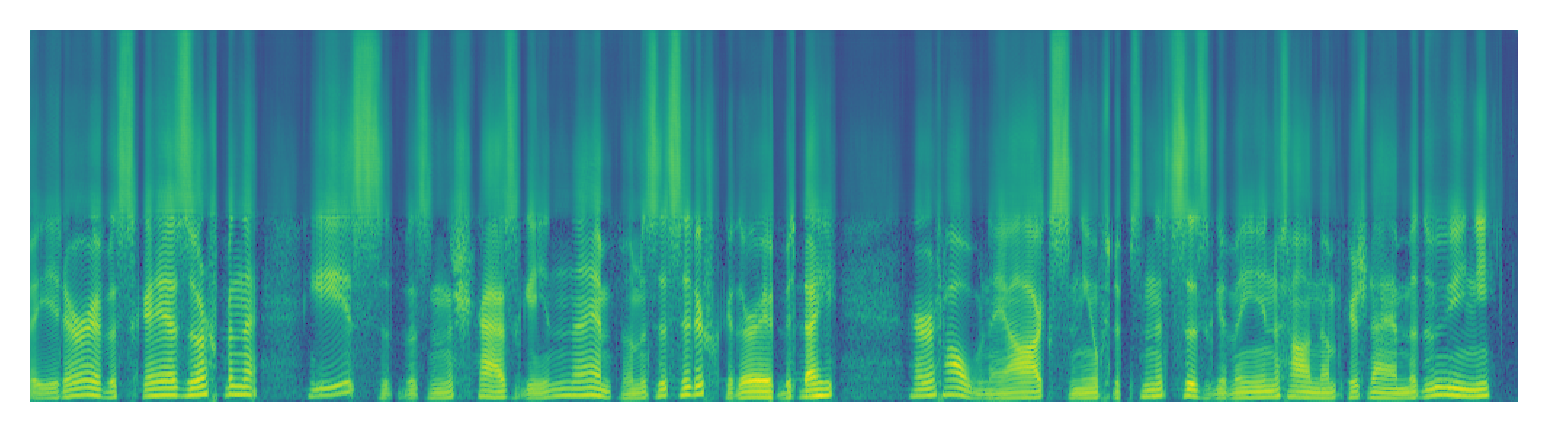 |
|
| U-Net | ||
 |
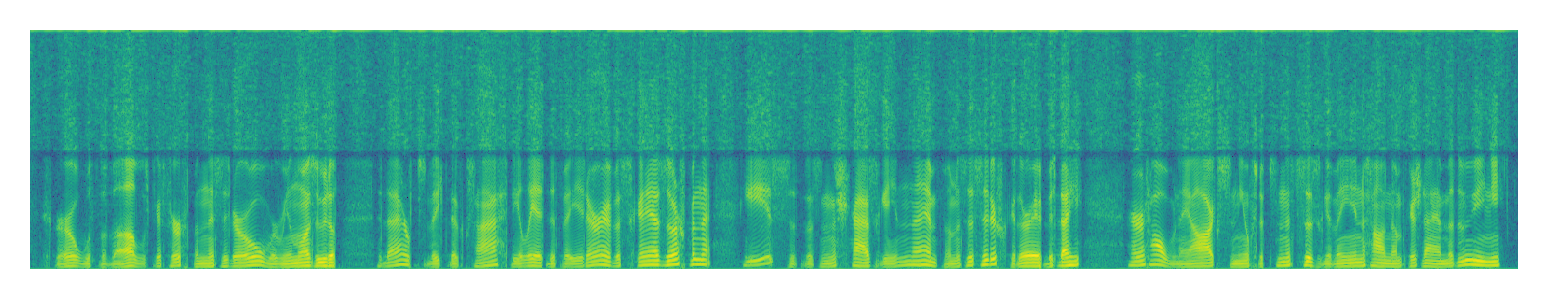 |
|
| NU-wave2 | ||
 |
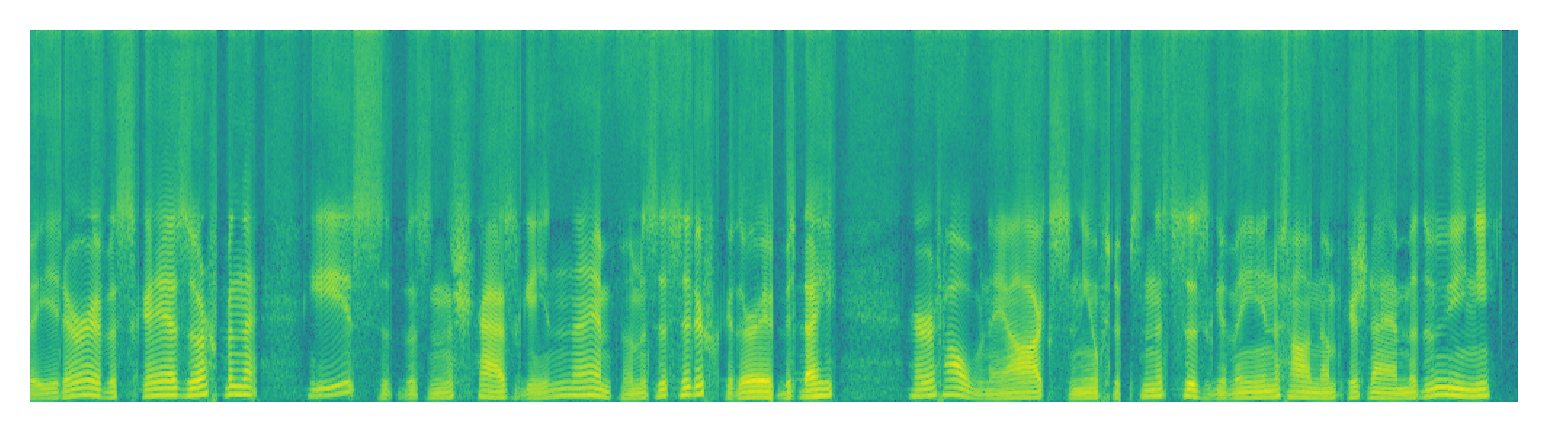 |
|
| Repaint (Our model) |
Unconditional diffusion produced plausible sounds from random noise
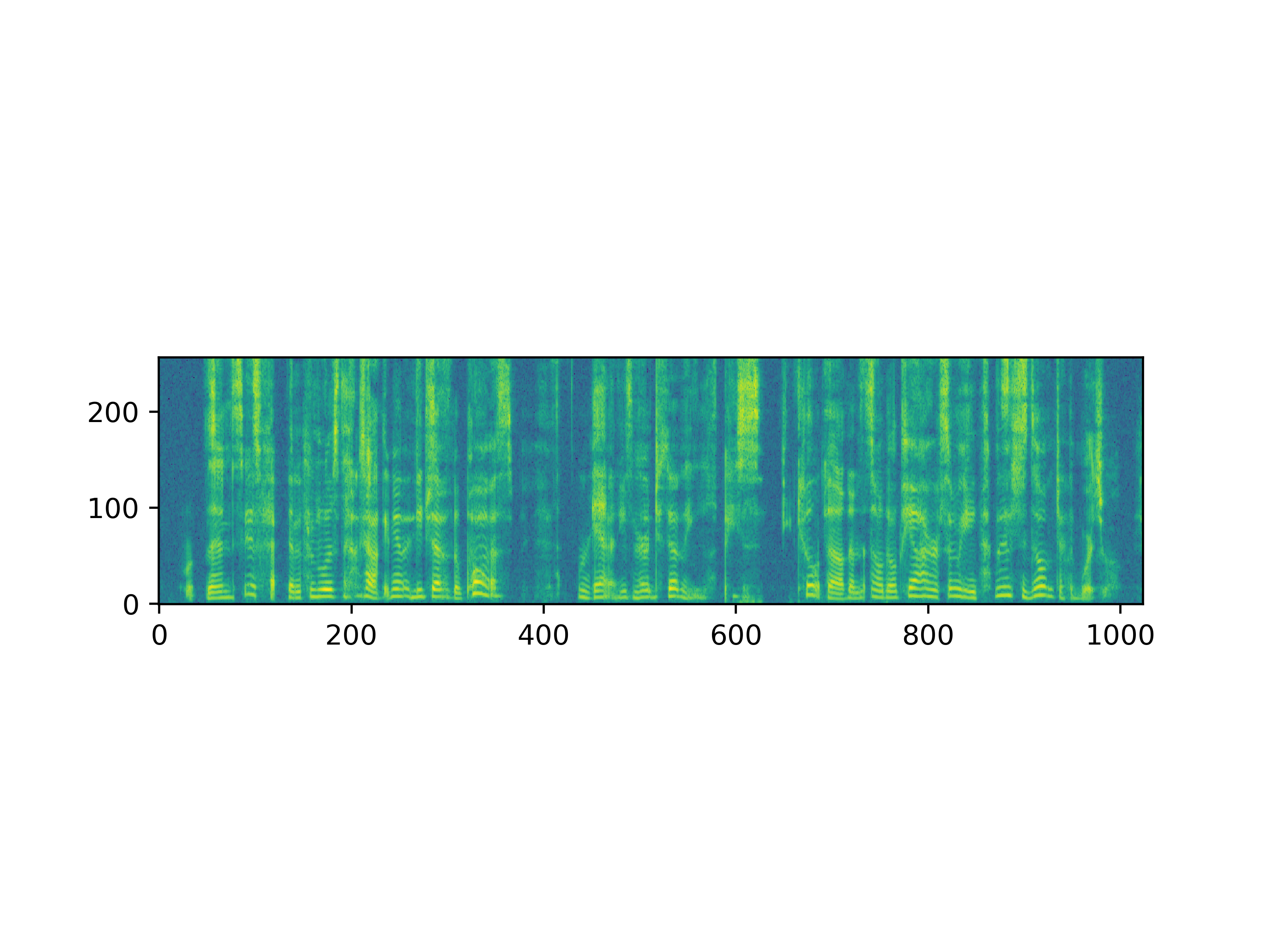 |
 |
|
| Unconditional diffusion |